| |
| |
Materials Informatics Laboratory |
 |
|
 |
| |
Development of new analysis and process for new materials and the
environment |
|
| |
| Our laboratory has developed new analysis
methods to use in manufacturing process for new materials and to detect
toxic substances in the environment using x-ray physics, spectroscopy,
physical chemistry, transport phenomenology and so on. We have also
designed nature-friendly manufacturing processes. Followings are some
typical examples of our recent activities. |
|
|
|
|
| |
 |
| • |
Development of measurement system for
electronic states using high resolution fluorescence spectroscopy. |
 |
| • |
Elementary analysis of toxic substances in incinerator
and in the environment using x-ray absorption spectroscopy. |
 |
| • |
Development of a combination system of scanning electron
microscope and synchrotron radiation, and x-ray analysis of yellow
sand. |
| • |
Development of small x-ray source device by new concept. |
| • |
Research for hydrogen absorbing materials and study on its mechanisms. |
| • |
Study of electronic structure of borides. |
| • |
Development and application of extended x-ray emission fine structure. |
| • |
Development and application of total reflection x-ray
photoelectron spectroscopy. |
| • |
Development of x-ray traveling wave spectroscopy. |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Academic staff |
|
| |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
| Professor : Kawai, Jun |
| |
| Research Topics |
| AnalitycalChemistry, Surface Analysis, X-Ray Spectroscopy,
Chemical Physics, Analytical Sciences, Heat and Mass Transfer,
Material and Chemical Information Analysis |
| |
| Contact / Office |
Room 831, School of Engineering Science Bldg, Yoshida Campus
TEL +81-75-753-5442 / FAX +81-75-753-5436
kawai.jun.3x kyoto-u.ac.jp kyoto-u.ac.jp |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
| Associate Professor : Yuge, Koretaka |
|
| |
| Contact / Office |
Room 829, School of Engineering Science Bldg, Yoshida Campus
TEL +81-75-753-5283 / FAX +81-75-753-5436
yuge.koretaka.4r kyoto-u.ac.jp kyoto-u.ac.jp |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
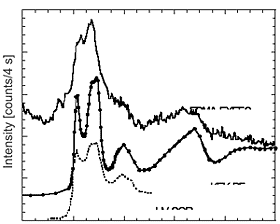
Development of extended x-ray emission fine structure. |
|
| |
X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) is well known to use measure
electronic structure of valence band of materials. We suggested that Extended
x-ray emission fine structure (EXEFS) show in x-ray fluorescence spectrum,
and observed that EXEFS spectrum is agree with XAFS spectrum. This EXEFS
spectroscopy is applied as an easy micro-prove analysis for small aerosol,
fly ash and so on. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
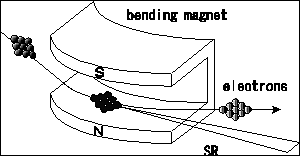
Investigation using synchrotron radiation |
|
| |
An electron traveling at almost the speed of light emits electromagnetic
radiation which covers a wide range of wavelengths from infrared/visible
light to x-ray regions. It is named “synchrotron radiation”.
Synchrotron radiation has many excellent features such as highly directional,
highly polarized, sharply pulsed and partly coherent.
Our laboratory study electronic structure of material and microanalysis
of aerosol in the atmosphere using synchrotron radiation. We also study
development of new experimental methods which introduce the features of
synchrotron radiation. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
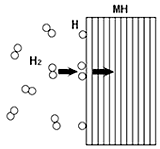
Study on mechanism of hydrogen absorption |
|
| |
| Hydrogen absorption
alloys are practical use as an anode of nickel hydrogen battery,
a hydrogen tank and so on, and are investigated to find higher
efficient alloys. The mechanism of hydrogen absorption into
the alloy is not fully understood.
We measure the properties of alloys as a function of the composition
and make clear the mechanism of hydrogen absorption using
extended Hückel method |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
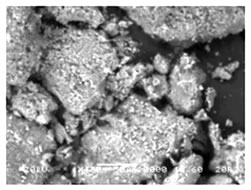
Subject |
|
| |
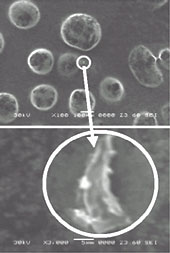
Yellow sands are generated around the western desert area in China
and transferred by the prevailing westerlies to the eastern Asian countries.
They are changed chemically during the flying over the industrial areas
and play an important role as one of various aerosol particles.
In our laboratory, it is intended by using SEM,
EMPA, synchrotron radiation to characterize the substances attached
on the yellow sand particles and to clarify the mechanism in the reaction
process of aerosol generation. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
 |
|
|